Bats have lengthy caught the imaginations of scientists and engineers with their unparalleled agility as well as handling features, attained by functionally flexible vibrant wing conformations in addition to more than forty active and easy joints on the wings. Nevertheless, their wing adaptability as well as intricate wing kinematics posture considerable technical difficulties for robot modelling, design, and control.
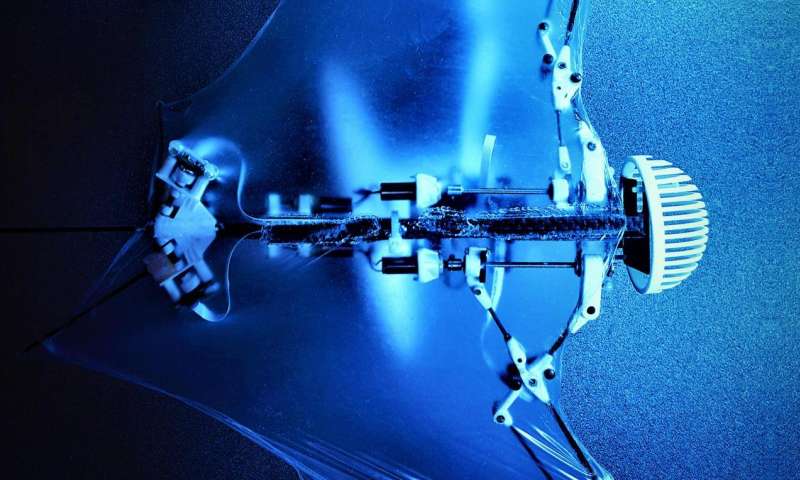
Scientists at the College of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and also Caltech have actually developed a self-contained robotic bat– dubbed Bat Robot (B2)– with soft, articulated wings that could mimic the essential trip devices of biological bats.
” Our job demonstrates one of the most sophisticated layouts to date of a self-contained flapping-winged airborne robotic with bat morphology that is able to carry out self-governing trip,” discussed Alireza Ramezani, a postdoctoral scientist at the University of Illinois who is the very first writer of the cover short article, “A Biomimetic Robot Platform to Research study Flight Field of expertises of Bats,” showing up in Scientific research Robotics on February 1. “It evaluates just 93 grams, with vibrant wing articulations as well as wing conformations much like those of organic bats.
Ramezani developed the model with his consultants Soon-Jo Chung– now an associate professor of aerospace at Caltech– as well as Seth Hutchinson at Illinois. These writers have actually been collaborating with Brown University professors Kenneth Breuer and also Sharon Swartz, that are specialists on bat trip.
” Our job introduces a design system to simulate the essential trip systems of organic bats,” said Chung, who is likewise a research study researcher at the Jet Propulsion Lab, which Caltech manages for NASA. “There is no reputable approach for reverse design the sophisticated mobility of bats.”
Arguably, bats have one of the most advanced powered flight system amongst animals, as evidenced by the shape-changing capacity of their wings. Their trip device entails greater than 40 sorts of joints that interlock the bones and muscle mass to each other creating a bone and joint system that can alter shape and also is capable of movement in several independent directions.
” The B2 has a variety of useful benefits over various other airborne robots, such as quadrotors,” said Chung. “Bats do have extra 40 active and easy joints; we lowered those numbers to 9 (5 active and 4 passive) joints in the B2 robotic. The compliant wings of a bat-like waving robot waving at reduced frequencies (7-10 Hz vs. 100-300 Hz of quadrotors) are naturally secure: due to the fact that their wings consist of mostly flexible materials and have the ability to collide with one another, or with barriers in their environment, with little or no damages.”
The B2 makes use of a morphing skeletal system variety as well as a silicone-based membrane skin that enables the robot to alter its articulated structure in mid-air without losing a reliable and smooth aerodynamic surface.
“Our trip control results are the first demo of using crooked wing folding of the main versatile wings to control the going of the airborne robot,” Ramezani included. “Its changing residential or commercial property can not be recognized with traditional materials (such as nylon or mylar) that are largely made use of in waving wing research. Non-stretchable materials resist the forelimb as well as leg movements in B2. Therefore, we covered the skeletal system of our robotic with a customized, ultra-thin (56 micron, silicone-based membrane layer that is made to match the elastic residential or commercial properties of biological bats’ membranes.
Bat-inspired airborne robotics likewise bring significant enhancements in power performance over present airborne robots. This schedules, at least partially, to their expressed soft wing architecture, and that wing flexibility enhances the motion of the robotic’s actuators.
“When a bat flaps its wings, it’s like a rubber sheet,” claimed Hutchinson, who is a teacher of electrical and computer design at Illinois. “It fills with air as well as deforms. And then, at the end of its down-stroke activity, the wing pushes the air out when it bounces back into place. So you get this big amplification of power that comes simply from the truth you are making use of versatile membrane layers inside the wing itself.
One potential application of B2 is to monitor building and construction websites. “Structure building projects are complicated, as well as hardly ever do they take place the means they are planned to occur,” Hutchinson said. “Keeping track of whether the structure is being assembled properly at the right time is not trivial. So the bat bots would fly about, pay attention, as well as contrast the building information version to the real structure that’s being constructed.
“As an example, for jobs that need the aerial robots to be fixed, our bat-inspired airborne robotics will eventually be able to perch, rather than floating, by taking advantage of unique frameworks in construction websites such as steel frames, side walls, and ceiling frames,” Chung stated. “This is an extra energy-efficient as well as reliable option because stationary hovering is hard for quadrotors in the visibility of even light wind– which is common for construction sites. Additionally, setting down or landing standard aircraft and quadrotors in such unusual areas is nearly impossible, because of their restricted control authority at sluggish electric motor rates as well as wind resistant couplings such as wall or ground effects.
Since the B2 does not make use of high-speed blades that produce loud, high-frequency noise, it is substantially much less invasive than quadrotors or other airborne robotics.
“Along with building and construction applications, we visualize robot flapping-wing robotics running in limited quarters with humans as well as beyond where people could go,” Chung noted. For example, an aerial robot furnished with a radiation detector, 3D cam system, as well as temperature level and also humidity sensors could check something like the Fukushima atomic power plants, where the radiation degree is too high for humans, or fly right into limited crawlspaces such as mines or fell down structures. Such highly manoeuvrable aerial robotics, with longer trip endurance, will also make breakthroughs in the surveillance and recovery of crucial facilities such as nuclear reactors, power grids, bridges, and also borders.
“B2 definitely could not be made use of for raising hefty packages yet, but a future version of Bat Bot might confirm the advantages of soft-winged flight, such as enhanced power efficiency as well as safety and security, for drone-enabled package distribution,” he stated.
“Lastly, this robotic can contribute to organic research studies on bat trip,” Hutchinson added. “The existing techniques for biology rely on vision-based movement capture systems that make use of broadband imaging sensors to tape-record the trajectory of joints and also limbs throughout bat trip. Although these techniques could properly assess the joint kinematics of bat wings in flight, they could not assist comprehend how particular wing activity patterns contribute to a specific flight maneuver of a bat. B2 could be used to rebuild trip maneuvers of bats by applying wing movement patterns observed in bat trip, therefore helping us comprehend the duty of the leading levels of freedom of bats.