[message_box color=”red”]An electrical current is a circulation of electriccharge. In electric circuits this cost is commonly lugged by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be brought by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and also electrons such as in a plasma.[/message_box]
Like a river current is the flow water of water particles, electric existing is the circulation of asked for bits. In this lesson, we’re visiting discover what electric current is, exactly what triggers it, which, unlike a water current, electric present does not constantly flow in one instructions.
The Flow of Electrons
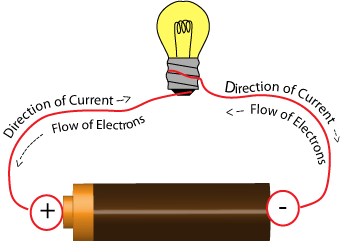
When you listen to the word ‘present,’ what does it make you consider? Probably water flowing down a stream? That’s a good association, since that’s specifically the factor electric current was given its name. Electrical current is quite just like a water current, simply as opposed to water particles moving down a river, charged fragments relocate down a conductor. In this driving lesson, we’re going to discover exactly what current is, just what induces it, as well as figure out that, unlike a water current, electric existing doesn’t constantly move in one instructions.
Current is the circulation of asked for bits via a carrying out tool, such as a cable. When we talk about electricity, the charged particles we’re referring to are almost always electrons. You see, the atoms in a conducting material have bunches of cost-free electrons that float about from atom to atom and also everywhere between. The movement of these electrons is arbitrary, so there is no circulation in any kind of provided direction. Nevertheless, when we use a voltage to the conductor, all the complimentary electrons will certainly move in the very same direction, developing a current.
An interested aspect of electric current is that while the electric radiation transfers through the conductor at nearly the rate of light, the electrons themselves move much, a lot slower. As a matter of fact, if you were to walk leisurely alongside a current bring cord, you would certainly be taking a trip more than 100 times faster than the electrons!
To view why this is, we could imagine an existing owning cord like a tube loadeded with marbles. The marbles stand for the electrons and also television represents the cable. If we placed a marble into one end of television, it presses on the very first marble, which presses on the next marble, and so on down the line. If we were standing at the various other end of the tube, we would view a marble leave at the same time the various other marble got in. In other words, the motion, and consequently the energy, was transferred virtually instantly. However, each specific marble simply relocated a small distance in television to transfer that energy. Due to the fact that the electrons in a cord do not need to take a trip quite far to transfer their energy to the following electron, their overall progress with the cord is fairly sluggish.
Direct and Alternating Current
There are two different sorts of present in widespread usage today. They are direct existing, shortened DC, and alternating current, abbreviated AC. In a direct present, the electrons flow in one direction. Electric batteries create a direct current since the electrons constantly move from the ‘negative’ side to the ‘good’ side.
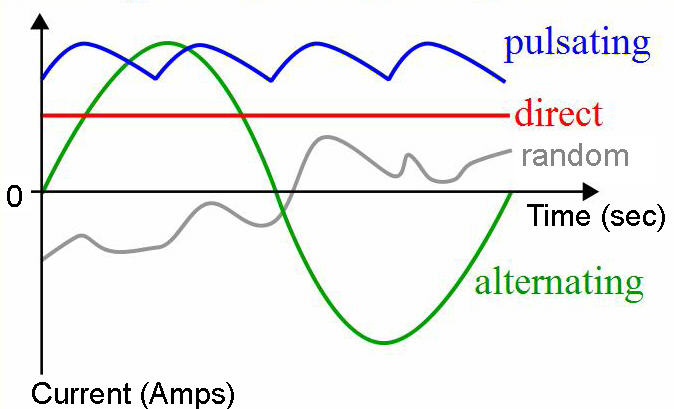
Alternating current, abbreviated Air Conditioning, presses the electrons backward and forward, altering the direction of the flow many times each second. In the United States, the present changes direction at a rate of 60 hertz, or 60 times in one secondly. The generators used in power plants to produce electrical power for your residence are developed to generate alternating current. You’ve most likely never ever observed the lights in your property in fact flicker as the existing adjustments instructions because it occurs too quick for our eyes to find.
So why do we require two kinds of current, as well as which one is better? Well, that’s a good question, as well as the fact that we’re still utilizing both types of existing ought to tell you that they both offer an objective. Back in the 19th century, it was recognized that to send power effectively over the far away between a power plant and also a home, it needed to be sent at an extremely high voltage. The problem was that sending actually high voltage right into a residence was extremely harmful for individuals living there.
The solution to this issue was to lessen the voltage right outside the home just before sending it inside. With the innovation that existed at the time, it was a lot easier to lessen the voltage of Air Conditioner compared to it was of DC, so A/C won out as the preferred type of current. To this day, we still utilize Air Conditioning for all of our long-distance power transmission, largely because of its capability to quickly change to various other voltages.
So why do we require DC at all? Well, primarily, it is essential to realize that we presently do not have any way to store electrical energy. ‘Yet, wait a min!,’ you might claim. ‘Exactly what about batteries? Don’t they store electrical energy?’ Well really, batteries transform electric radiation and store it as chemical radiation. As we discussed earlier, batteries simply develop DC, as well as then, can just be charged with DC. That implies that Air Conditioner has to first be transformed to DC just before it can be utilized with an electric battery. Till an Air Conditioner electric battery is invented, DC will constantly be a requirement.
